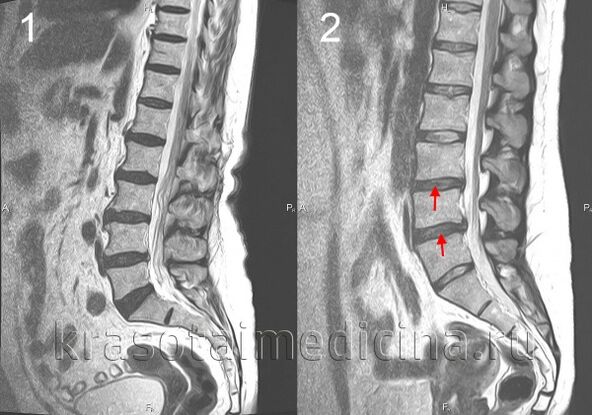
Vertebral spine osteochondrosis is a chronic disease in which degenerative changes in vertebrae and intervertebral discs occur between them.Depending on the place of damage to the spine, they distinguish: cervical region osteochondrosis, thoracic osteochondrosis and lumbar region osteochondrosis.To diagnose spine osteochondrosis, radiography is required and, in the case of its complications (eg intervertebral disc hernia) - MRI RESONANCE OF THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN.In the treatment of spine osteochondrosis, along with drug methods, it is widely used, reflexology, massage, manual therapy, physiotherapy and physiotherapy exercises.
Etiology and pathogenesis
At one degree or another, spine osteochondrosis develops in all aged people and is one of the body's aging processes.Anterior or posterior, atrophic changes occur in the intervertebral disc, however, lesions, diseases and various column overloads contribute to the previous occurrence of osteochondrosis.The most common osteochondrosis of the cervical region and lumbar spine osteochondrosis.
About 10 osteochondrosis theories were developed: vascular, hormonal, mechanical, hereditary, allergic and allergic and others.But none of them give a complete explanation of the changes that occur in the spine, but are complementary.
It is believed that the main point in the occurrence of osteochondrosis is the constant overload of the vertebral motor segment consisting of two adjacent vertebrae.This overload can occur as a result of an engine stereotype - posture, an individual way of sitting and walking.The disorders of the posters, sitting in the wrong pose, walking with an unequal column of the spine spine cause an additional load on the discs, ligaments and muscles of the spine.The process may aggravate due to the characteristics of the spine structure and the insufficiency of the tropism of its tissues due to hereditary factors.Most of the time, the addictions of the structure are found in the cervical region and lead to vascular disorders and the initial appearance of signs of cervical spine osteochondrosis.
The occurrence of lumbar osteochondrosis is more often associated with its overload during inclinations and elevators of gravity.A healthy intervertebral disc can withstand significant loads due to the hydrophilicity of the pulse core located in its center.The core contains a large amount of water and fluids, as you know, are little compressed.Breaking a healthy intervertebral disc can occur with a compression of over 500 kg, while the disc changed as a result of osteochondrosis is torn with a 200 kg compression.A 200 kg load is experimenting with a lumbar of a person's spine of a person weighing 70 kg when it maintains a 15 kg load in the body's tilt position before 200. Such a large pressure is due to the low size of the pulp core.With an increase in inclination to 700, the load on intervertebral discs will be 489 kg.Therefore, the first clinical manifestations of lumbar spine osteochondrosis occur during or after the lifting of weights, performing housework, weeds in the garden, etc.
The destruction of the connective tissue of the fibrous ring of the disc, ligaments and capsules of the facet joints causes the reaction of the immune system and the development of aseptic inflammation with the swelling of the facet joints and the surrounding tissues.Due to the displacement of the vertebral bodies, the facet joint capsules are stretched and the altered intervertebral disc is not so firmly fixed by the bodies of the neighboring vertebrae.The instability of the spine segment is formed.Due to instability, it is possible to violate the spinal nerve with the development of root syndrome.With cervical spine osteochondrosis, this often occurs during head curves, with osteochondrosis of the lumbar region - during the inclinations of the body.It is possible to form a functional block of the vertebral engine segment.It is due to the reduction of compensation of the vertebral muscles.
The herniated intervertebral disc is formed when the disc changes backwards, the posterior rupture of the longitudinal ligament and the disc protrusion in the spinal canal occurs.If, at the same time, the core of the disc is squeezed on the cerebrospinal fluid, this hernia will be called exploding.The severity and duration of pain with such a hernia are much longer than with not exploded.The herniated disc can cause root syndrome or spinal cord compression.
With osteochondrosis, bone tissue growth occurs with the formation of osteophytes - bone consequences in the bodies and processes of vertebrae.Osteophytes can also cause spinal cord compression or cause root syndrome development.
Spine osteochondrosis symptoms
The main symptom of spine osteochondrosis is pain.The pain can be acute with high intensity, intensifies with the lowest movement in the affected segment and therefore causes the patient to take a forced position.Therefore, with cervical spine osteochondrosis, the patient holds the head in the less painful pose and cannot turn, with thoracic osteochondrosis, the pain increases even with deep breathing and lumbar region osteochondrosis, it is difficult to sit, climb and walk.This pain syndrome is characteristic of compressing the spinal spine.
In approximately 80% of cases, there is an opaque pain of a constant nature and moderate intensity.In these cases, after the examination, the doctor should differentiate the manifestations of osteochondrosis from the myositis spine from the back muscles.Idiotic pain in osteochondrosis is due to excessive muscle tension, maintaining the affected vertebral motor segment, inflammatory changes or significant stretching of the intervertebral disc.In patients with such pain, a forced position is absent, but the restriction of movements and physical activity is revealed.Patients with cervical spine osteochondrosis avoid steep curves and inclinations with the head, with slowly osteochondrosis - sit slowly and rise, avoiding the inclination of the body.
Column osteochondrosis complications
The complications of osteochondrosis are associated with the hernia of the intervertebral disc.This includes compression of the spinal cord, characterized by numbness, the weakness of certain muscle groups of the extremities (depending on compression level), leading to the appearance of paresis, muscle atrophy, a change in tendon reflexes, urination and defecation.Intervertebral hernia can cause artery compression by feeding the spinal cord with the formation of ischemic areas (spinal cord infarction) with the death of nerve cells.This is manifested by the appearance of a neurological deficit (impaired movements, sensitivity, trophic disorders) corresponding to the level and prevalence of ischemia.
Spine osteochondrosis diagnosis
The diagnosis of spinal osteochondros is performed by a neurologist or vertebrologist.In the early stage, the spine radiography is performed in 2 projections.If necessary, they can photograph a separate spinal segment and fire in additional projections.For the diagnosis of intervertebral hernias, the state of the spinal cord is used and detect complications of osteochondrosis, magnetic tomography and resonance (magnetic resonance imaging of the spine).An important role is played by magnetic resonance imaging in the differential diagnosis of osteochondrosis and other spinal diseases: tuberculosis spondylitis, osteomyelitis, tumors, spontaneous ankylosing, rheumatism, infectious lesions.Sometimes, in cases of complicated osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, syringomyelia exclusion is required.In some cases, if magnetic resonance imaging is impossible, myelography will be shown.
A directed study of the affected intervertebral disc is possible using discography.Electrophysiological studies are used to determine the degree and location of nerve road damage to monitor the process of its restoration during therapy.
Treatment of spine osteochondrosis
In the acute period, peace is shown in the affected vertebral motor segment.For this purpose, with cervical spine osteochondrosis, the fixation is used using a Chantz necklace, with lumbar region osteochondrosis - bed rest.Fixation is also required for cervical region osteochondrosis with vertebral segment instability.
In the drug therapy of osteochondrosis, non -anti -inflammatory drugs (NSAID) is used: diclofenac, nimesulide, lornoxicam, meloxicam.With intense pain syndrome, painkillers are shown, for example, an analgesic central action of FluPortin.To relieve muscle tension, muscle relaxants - tolperisone, tizanidine are used.In some cases, it is advisable to prescribe anticonvulsant medications - carbamazepine, gabapentin;Antidepressants, among whom preference is given to the inhibitors of the reverse capture of serotonin (Cersertalin, Paroxetine).
In the case of a root syndrome, hospital treatment is indicated.Local glycocorticoid introduction is possible, edema treatment, traction use.In the treatment of osteochondrosis, physiotherapy, reflexology, massage, physical therapy exercises are widely used.The use of manual therapy requires clear observance of the technique of its implementation and special caution in the treatment of cervical spine osteochondrosis.
Spine operations are mainly indicated with significant compression of the spinal cord.It consists of removing the hernia from the intervertebral disc and the decompression of the spinal canal.It is possible to perform microdisectomy, disk laser reconstruction, disc replacement affected by an implant, stabilization of the spine segment.